|
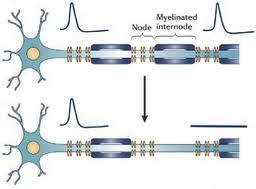
Abnormal Sensations in MS. Why do they occur and what do they mean? Abnormal sensations and pain are a common experience for people with MS. To understand this a little better, I need to begin with a short explanation of how the nervous system works. The images above are cross sectional depictions of two neurons and their associated axon. Neurons, as you can see, are strange looking cells with tentacles (axons and dendrites) that reach out and connect with other neurons in defined circuits. The connections made by these neurons are the means by which your nervous system receives information, interprets and manipulates information and acts on information. This information may come in the form of sights, sounds, tastes, smells, sensations or language. The information flow can also start from spontaneously generated thought and contemplation. The myelin that is damaged in MS is shown in blue (called the myelinated internode in the picture) wrapped around segments of the axon (shown in blue green) with gaps between the myelinated internode that are called the Nodes of Ranvier (labeled Node in the picture). As you may know it is common in medicine to name things after their founder and a French physician in the late 19th and early 20th century named Ranvier discovered this peculiar feature of our nervous systems. The top image is a normal neuron-axon unit and the lower image depicts a neuron-axon unit that has been stripped of myelin in an area but with no permanent damage to the axon. Now why is this a problem?
The difficult question is whether these new sodium channels that sprout all axons are harmful. There is some research that indicates that the effects of these sodium channels may lead to permanent damage to the neuron, but attempts so far to prevent this from occurring by administering drugs that block sodium channels have not been successful.
Margaret Sessions
8/2/2014 12:03:09 am
Does this mean if we lower our sodium intake it would help eliminate or at least slow these attacks?
Dr Kinkel
8/5/2014 03:13:38 am
The easy answer is no; your body regulates sodium concentration within a tight range by telling the kidneys to either retain water or excrete more water. If you were to take in more or less sodium in your diet, your kidneys would simply adjust normally. Even if you could lower sodium levels (which you could temporarily) this would have very harmful effects on your nervous system Comments are closed.
|
DISCLAIMER:
The medical information and opinions on this site are provided as an information resource only, and are not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. The information and opinions expressed do not create any patient-physician relationship, and should not be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. Archives
January 2020
Categories
All
|
- Home
- About Us
- Virtual MS Center
- News & Resources
- Seminar Registration
- Health & Wellness
- Blogs
- About MS
-
Symptoms
- Balance and Walking Issues
- Breathing/Respiratory
- Bowel Dysfunction
- Cognitive Dysfunction
- Crying/Laughing Uncontrollably (PBA)
- Depression and Anxiety
- Dizziness/Vertigo
- Dysphagia
- Fatigue
- Foot Drop
- Hearing or Smell or Taste Changes
- Heat Sensitivity
- Leg Weakness
- Loss of Hand Dexterity and Coordination
- Memory and Mutliple Sclerosis
- Migraines
- Numbness/Tingling/Altered Sensation
- Nystagmus and Oscillopsia
- Pain
- Sexual Dysfunction
- Sleep Issues
- Spasticity/Spasms/Cramps
- Speech/Swallowing
- Urination/Bowel Problems
- Vision
- MS Clinics
- MS Topics
- Register With Us
- Terms of Use/Privacy/HIPAA
- MS HealthCare Journey

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
